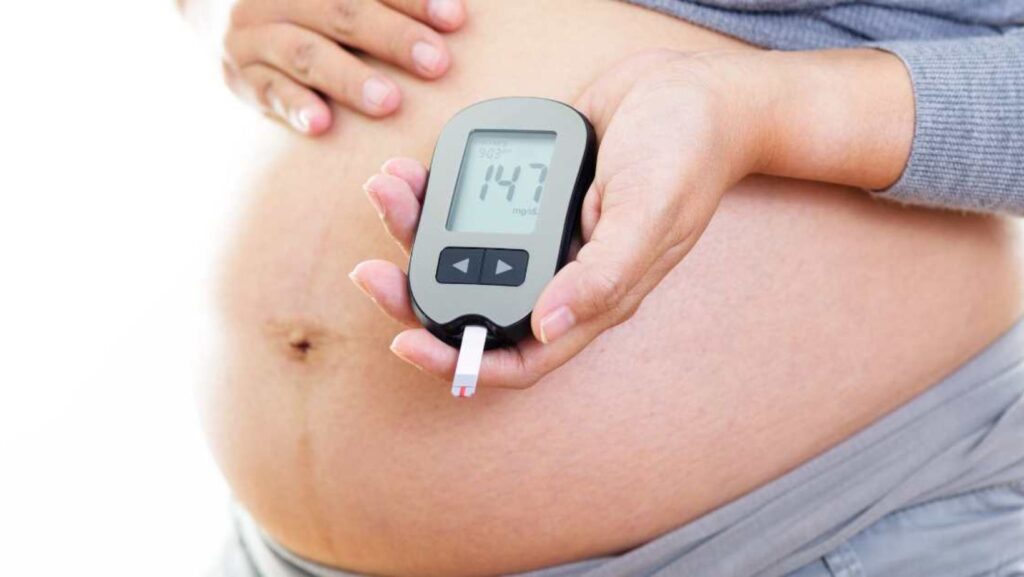
When is the Glucose Test Pregnancy
As an expert, I know that the glucose test during pregnancy is typically done between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation. This screening test helps healthcare providers exclusive deals on monitor glucose levels to ensure the mother does not have gestational diabetes, a condition that can develop during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes can pose risks to both the mother and baby if left untreated.
During this test, pregnant individuals are asked to drink a sugary solution. After waiting for about an hour, blood is drawn to measure blood sugar levels. Depending on the results, further testing may be required. It’s important for expectant mothers to follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding prenatal screenings like the glucose test to promote a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
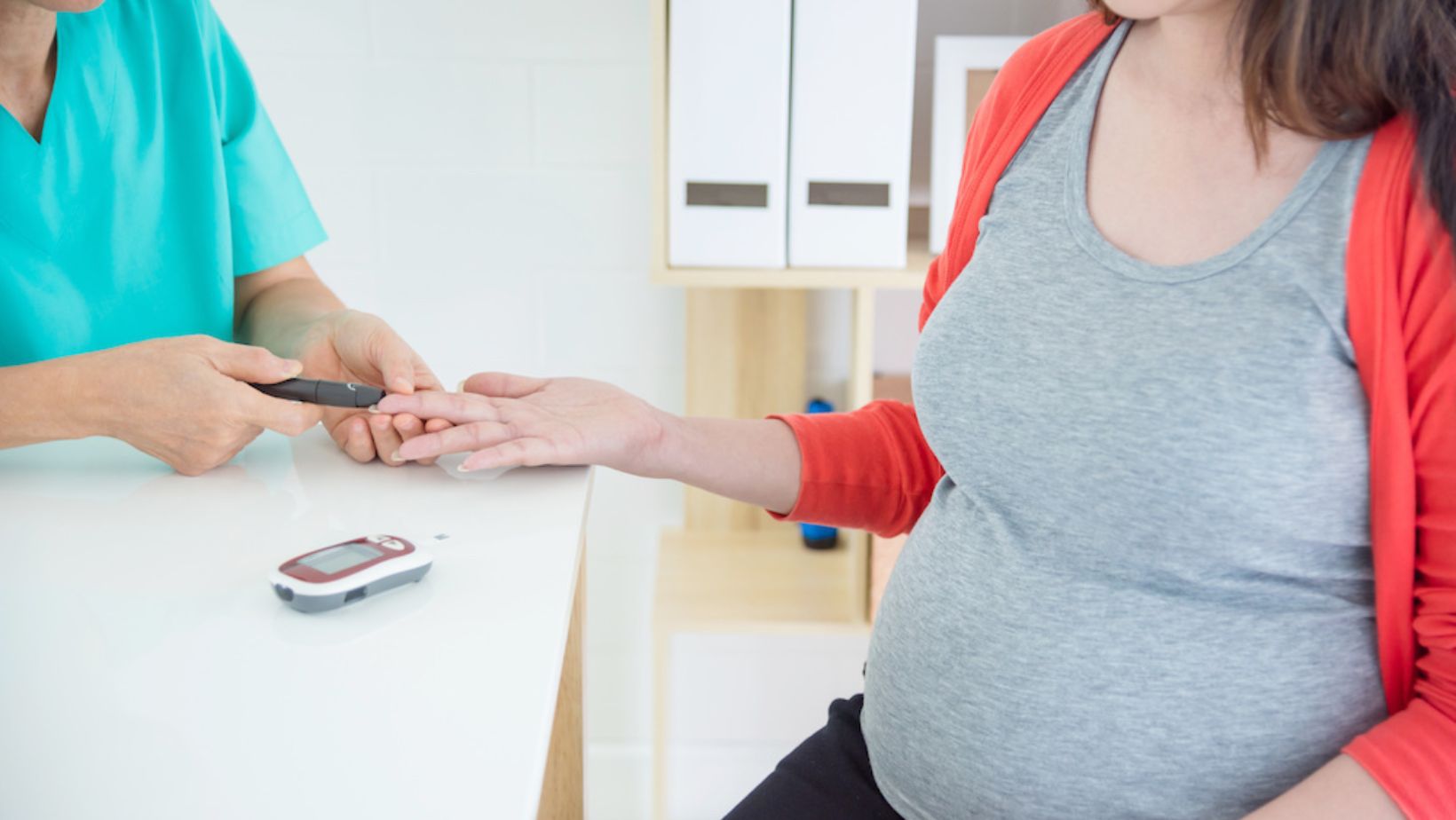

What is the Glucose Test in Pregnancy?
When it comes to monitoring blood sugar levels during pregnancy, healthcare providers often recommend a Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) or Glucose Screening Test. This test helps assess how well a pregnant individual’s body processes sugar. The main purpose is to detect gestational diabetes, a condition that can develop during pregnancy and affect both the mother and baby.
During this test, which usually occurs between 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy, the individual consumes a sugary drink containing glucose. Blood samples are then taken at specific intervals to measure how the body metabolizes sugar. Elevated glucose levels may indicate potential gestational diabetes, requiring further evaluation and management.
It’s important for individuals undergoing this test to follow any preparation instructions provided by their healthcare provider. Typically, these guidelines include fasting before the test and avoiding certain foods or medications that could interfere with the results. While some may find drinking the sweet solution unpleasant due to its high sugar content, it is essential for accurate testing.
Understanding the significance of the Glucose Test in Pregnancy can empower expectant parents to take proactive steps towards maintaining their health and that of their unborn child. Early detection of gestational diabetes through this screening enables timely interventions, such as dietary changes or insulin therapy if necessary, reducing risks associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels throughout pregnancy.
When is the Glucose Test Administered During Pregnancy?
When it comes to pregnancy, many women wonder about the timing of the glucose test. The Glucose Challenge Test (GCT) is typically performed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. It’s a common screening test used to check for gestational diabetes.
During this period, the body goes through significant changes, making it crucial to monitor blood sugar levels closely. Gestational diabetes can develop when the body struggles to produce enough insulin to meet the extra demands of pregnancy. Detecting and managing this condition early is vital for both maternal and fetal health.
Most healthcare providers recommend taking the glucose test during the second trimester of pregnancy because this is when gestational diabetes often starts to manifest. By identifying any issues early on, doctors can work with patients to create a care plan that ensures a healthy outcome for both mother and baby.
Ensuring proper timing for the glucose test allows healthcare professionals to intervene promptly if needed, reducing potential risks associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Regular prenatal check-ups play a key role in monitoring maternal health throughout pregnancy, including screening for conditions like gestational diabetes.
As we wrap up our discussion on when the glucose test is conducted during pregnancy, it’s evident that this screening plays a crucial role in monitoring maternal health and ensuring the well-being of both the mother and baby. By assessing blood sugar levels, healthcare providers can identify potential risks early on and implement appropriate interventions to manage gestational diabetes.


